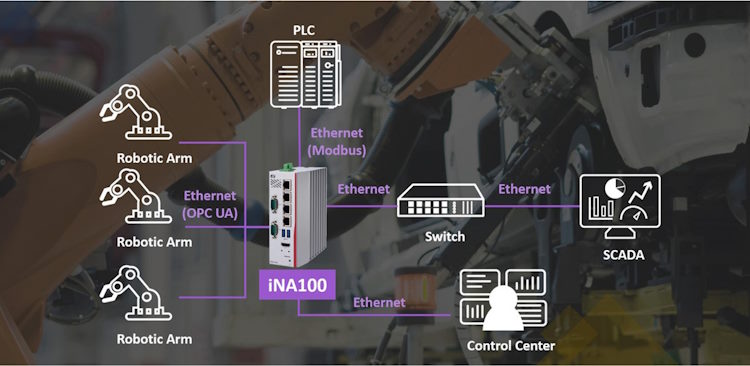
Is Data security concern become the road block to Industrial Transformation? That is the topic that we are discussing this round in our Episod 46 live chat on 26th of April 2024.
What challenges arise regarding data security in the realm of industrial transformation? SME manufacturers are particularly concerned about exposing their data to the cloud or exchanging data over the internet.
Cybersecurity threats are diverse and constantly evolving, but here’s an overview of some common ones:
Phishing Attacks: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information (such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details) by impersonating a trustworthy entity.
Malware: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware.
Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security, often through psychological manipulation or impersonation.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: Overloading a system or network with excessive traffic to disrupt its normal functioning, making it inaccessible to legitimate users.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Intercepting and possibly altering communication between two parties without their knowledge, allowing attackers to eavesdrop or manipulate data.
SQL Injection: Exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications to inject malicious SQL code, enabling attackers to access, modify, or delete data stored in databases.
Zero-Day Exploits: Exploiting previously unknown vulnerabilities in software or hardware before a patch or fix is available, making them particularly dangerous as they leave no time for defense measures to be implemented.
Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent actions by individuals within an organization, such as employees, contractors, or partners, who misuse their access privileges to steal data, sabotage systems, or cause harm.
Credential Theft: Unauthorized acquisition of usernames, passwords, or other authentication credentials, often through phishing, keylogging, or exploiting weak authentication mechanisms.
Cryptojacking: Illicit use of someone else’s computing resources to mine cryptocurrency without their consent, often accomplished through malware or compromised websites.
IoT (Internet of Things) Vulnerabilities: Exploiting security weaknesses in connected devices and systems, including smart home appliances, industrial sensors, and medical devices, to gain unauthorized access or disrupt operations.
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access, disclosure, or theft of sensitive or confidential data, which can result in financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
These are just some of the many cybersecurity threats organizations and individuals face today. Staying informed about emerging threats and implementing robust security measures are essential for protecting against cyber attacks.
Axiomtek offers Network appliances that allow you build your own cybersecurity system with the security software loaded, one of them is Pfsense. Network appliances like NA362 in our series of product is able to offer you great connectivity and performance.
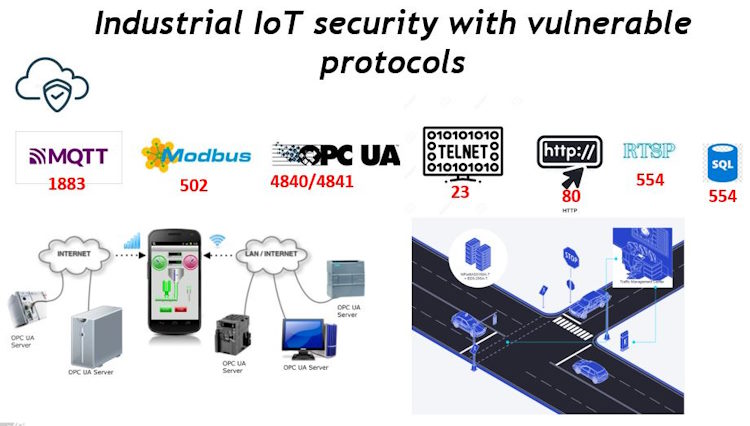
Below are some of the port number listing of available TCPiP connection used in industrial applications:-
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): Port 1883 (non-encrypted MQTT) and port 8883 (MQTT over TLS/SSL).
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Port 80 (HTTP) and port 443 (HTTP over TLS/SSL, commonly known as HTTPS).
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): Port 443.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Port 25 (SMTP) and port 587 (SMTP submission, commonly used for email clients to submit messages to the mail server).
DNS (Domain Name System): Port 53 (DNS).
FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Port 21 (FTP control) and port 20 (FTP data).
SSH (Secure Shell): Port 22 (SSH).
Telnet: Port 23 (Telnet).
SMB (Server Message Block): Port 445 (SMB over TCP/IP).
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol): Port 3389 (RDP).
These are just a few examples of major TCP services and their associated port numbers. It’s important to note that these services may use additional ports for specific purposes or configurations.
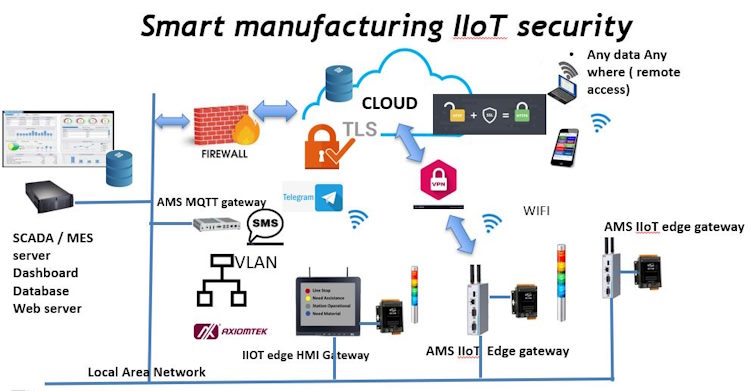
In the industrial IoT network in the smart manufacturing, data security is one of key concern especially when the data exchange over internet take place. Above diagram show some main protection are in place to secure the Digital transformation network.
Firewall will be main gateway before entering or exiting the local area network to the cloud.
Data exchange over MQTT are secured via the TLS or SSL encryption with certificate that is where all the shop floor data are being collected and published to the Cloud. all the web access will be done via a https with encryption. In some of the remote area data transmission over MQTT via the NR300 and NR500 4G Gateway router system, all the connected are fully protected with the SSL and certificate and password as well.
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) functionality plays a crucial role in enhancing security within a local area network (LAN) by providing segmentation and isolation of network traffic. Here’s how VLANs contribute to network security:
Segmentation: VLANs allow the logical segmentation of a physical LAN into multiple virtual LANs, each functioning as a separate broadcast domain. This segmentation helps to contain network traffic within specific groups or departments, preventing unnecessary exposure of sensitive data to other parts of the network.
Isolation: VLANs enable the isolation of network resources and devices based on logical groupings rather than physical locations. This isolation helps to minimize the risk of unauthorized access or attacks spreading across the network. For example, critical servers and devices can be placed in separate VLANs to limit access only to authorized users or systems.
Traffic Control: VLANs provide granular control over network traffic by allowing administrators to define access policies and enforce security measures at the VLAN level. This includes setting access control lists (ACLs) to filter traffic between VLANs, implementing quality of service (QoS) policies to prioritize certain types of traffic, and applying security policies such as firewall rules and intrusion detection/prevention systems.
Reduced Broadcast Domain: By dividing the network into smaller broadcast domains, VLANs help reduce the amount of broadcast traffic that reaches every device on the network. This can improve network performance and security by minimizing the impact of broadcast storms and other broadcast-related issues.
Flexibility and Scalability: VLANs provide flexibility and scalability in network design and management. Administrators can easily add, remove, or reconfigure VLANs to adapt to changing network requirements without the need to physically rewire the network infrastructure.
Overall, VLANs enhance network security by providing segmentation, isolation, traffic control, and scalability, allowing organizations to better manage and protect their network resources and data.
To enjoy watching our channel at Youtube. do click the link below:-
https://youtube.com/live/LtFple-UEQs