What are the applications of Digital Twin? Can Digital Twin helps in the Manufacturing? The discussion continued in the “Sembang AIoT” session episod 45 on 19th of April 2024 presented by the AIoT Team leaders Mr. CC Lee and Tan Kien Leong.
What is Digital Twin?
Imagine having a virtual clone of a real-life object, like a car or a building. This virtual copy is constantly updated with real-time data from its real counterpart, so you can monitor, analyze, and even predict its behavior or performance without actually touching or seeing the physical object. It’s like having a magical mirror that shows you everything about something, even if it’s miles away! That’s basically what a digital twin is: a virtual representation of a physical thing, helping you understand and manage it better.
In manufacturing, digital twins are used extensively for optimization across various stages of the production process. Here’s how:
Design and Prototyping: Digital twins help engineers optimize product designs by simulating how different configurations perform in virtual environments. This allows them to identify and rectify potential issues early in the design phase, saving time and resources.
Production Planning: Manufacturers use digital twins to simulate production processes, including material flows, machine operations, and workforce scheduling. By analyzing different scenarios, they can optimize production schedules, minimize downtime, and maximize resource utilization.
Predictive Maintenance: Digital twins of manufacturing equipment continuously collect real-time data on performance metrics such as temperature, vibration, and energy consumption. By analyzing this data and comparing it with expected behavior, manufacturers can predict when equipment is likely to fail and schedule maintenance proactively to prevent costly unplanned downtime.
Quality Control: Digital twins enable real-time monitoring and analysis of product quality parameters throughout the manufacturing process. By comparing virtual simulations with actual production data, manufacturers can identify deviations and take corrective actions to ensure consistent product quality.
Supply Chain Optimization: Digital twins help optimize supply chain operations by simulating inventory levels, transportation routes, and demand forecasts. Manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, minimize lead times, and optimize inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs.
Overall, digital twins provide manufacturers with valuable insights into their operations, allowing them to optimize processes, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. By leveraging real-time data and simulation capabilities, manufacturers can make informed decisions to stay competitive in today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape.
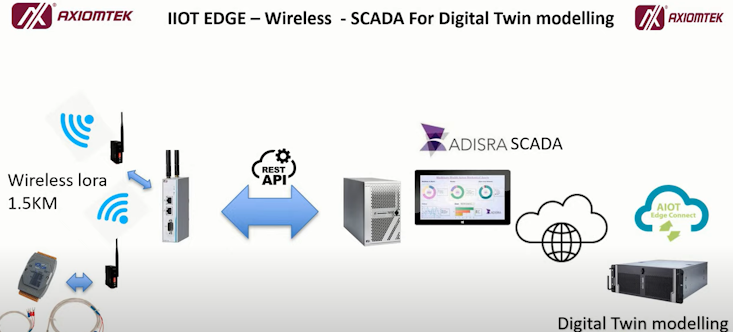
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) plays a crucial role in facilitating digital twins by providing the necessary data and connectivity infrastructure. Here’s how IIoT enables and enhances digital twins:
Data Collection: IIoT sensors and devices collect real-time data from various assets, machines, and processes in the manufacturing environment. These sensors monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and energy consumption, providing a continuous stream of data that is essential for creating and updating digital twins.
Connectivity: IIoT networks enable seamless connectivity between sensors, devices, and computing systems, allowing data to be transmitted securely and reliably. This connectivity ensures that data from different sources can be aggregated and analyzed to create comprehensive digital representations of physical assets and processes.
Data Integration: IIoT platforms integrate data from diverse sources, including sensors, SCADA systems, MES systems, and ERP systems. This integrated data provides a holistic view of the manufacturing operations, enabling more accurate and detailed digital twins.
Real-time Monitoring and Control: IIoT enables real-time monitoring and control of assets and processes, allowing operators to visualize the performance of digital twins and make timely adjustments to optimize operations. This real-time visibility enables proactive decision-making and enhances operational efficiency.
Predictive Analytics: IIoT data combined with advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and AI, enable predictive maintenance and process optimization. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns and anomalies, predictive models can anticipate equipment failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and improve overall performance.
Remote Management and Collaboration: IIoT enables remote access and management of assets and processes, allowing operators and engineers to interact with digital twins from anywhere at any time. This remote capability facilitates collaboration, troubleshooting, and decision-making, even across distributed or remote manufacturing facilities.
Overall, IIoT provides the foundational infrastructure and capabilities necessary for creating, updating, and leveraging digital twins in manufacturing. By integrating real-time data, connectivity, and analytics, IIoT enhances the accuracy, reliability, and value of digital twins, enabling manufacturers to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and drive innovation.

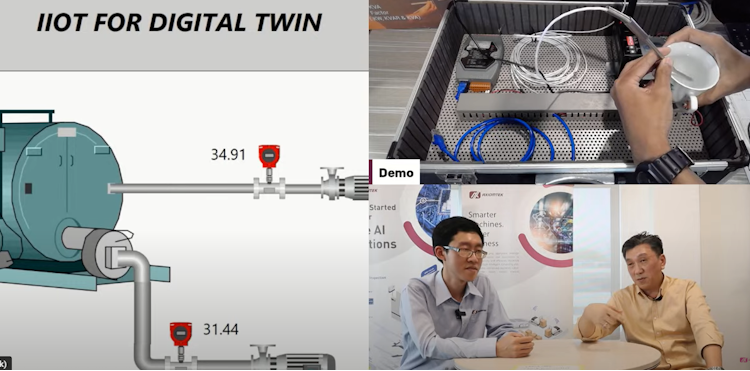
Demonstration of Axiomtek IIOT edge Gateway act as a data concentrator linking to the temperature sensing probe with Lora Radio transceiver.
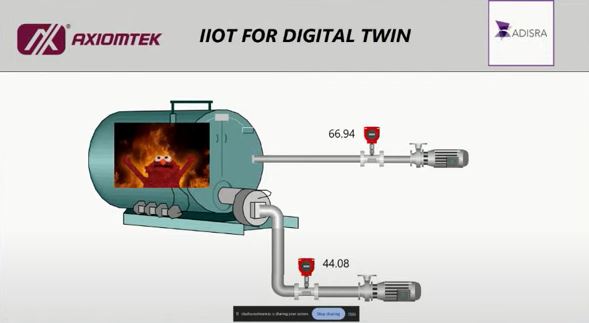
Adisra SCADA software act as a Fog node in centralized data collection and monitoring station. Industrial IOT Edge HMI can be also a displaying and monitoring panel.The data can then be piped to the Digital Twin model.
- To watch the live session : click the link below:-
Find out more in the previous chapter on the following subjects:-
Pingback: AioT driven Power and Energy monitoring - Axiomtek industrial PC Malaysia
Pingback: ESG Strategy on 24/7 Operation: Low Power Solutions - Axiomtek industrial PC Malaysia
Comments are closed.